Did you know that the incidence of thyroid disease has been increasing over the past few years? Statistics show that 12 percent of the United States population has been diagnosed with a thyroid abnormality. This includes 20 million Americans who undergo routine physical examination, laboratory tests, and treatment due to thyroid dysfunction.
Hypothyroidism is one of the most common thyroid diseases in the U.S. Due to the rising prevalence of hypothyroidism, it is crucial to determine the causes, symptoms, and management of the disease to ensure immediate diagnosis. Immediately go to reputable health centers in Boise, such as RedRiver Health and Wellness Center, if you notice any of the symptoms of hypothyroidism.
What is hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is a condition wherein the thyroid gland is unable to function optimally or secrete hormones that are vital in proper body function. The thyroid hormone facilitates metabolism, digestion, brain development, and maintenance of bone density. Therefore, low thyroid hormone levels can significantly impair normal activities and organ development.
What causes hypothyroidism?
Several conditions may cause hypothyroidism. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is the most common cause of low thyroid hormone levels in developed countries. It comprises more than half of cases of hypothyroidism among females in the U.S. This autoimmune condition occurs due to abnormal activation of immune cells that trigger the destruction of healthy thyroid tissue. As a result, the limited number of healthy cells is rendered unable to produce adequate hormone levels.
Surgical removal of a hyperactive thyroid is another common cause of hypothyroidism. In cases of goiter, hyperthyroidism, and thyroid malignancy, you may undergo operative removal of the thyroid. However, if the entire thyroid tissue is removed, you may experience symptoms of hypothyroidism.
Medication intake is a common extrinsic cause of thyroid destruction. Some drugs that cause thyroid insult include lithium, amiodarone, and interferon alpha. Since these medications have adverse effects on the thyroid, gradual tissue destruction may ensue.
What are the symptoms of hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is a condition that has distinct signs and clinical manifestations. This may include unprovoked fatigue, severe body weakness, and crampy muscle pain. Since the thyroid hormone plays a pivotal role in metabolism, patients with hypothyroidism have a higher risk of gaining excessive weight. Dry skin and hair are also expected during the latter course of the illness. You also develop a higher risk of osteoporosis, menstrual irregularities, and memory loss.
How is hypothyroidism diagnosed?
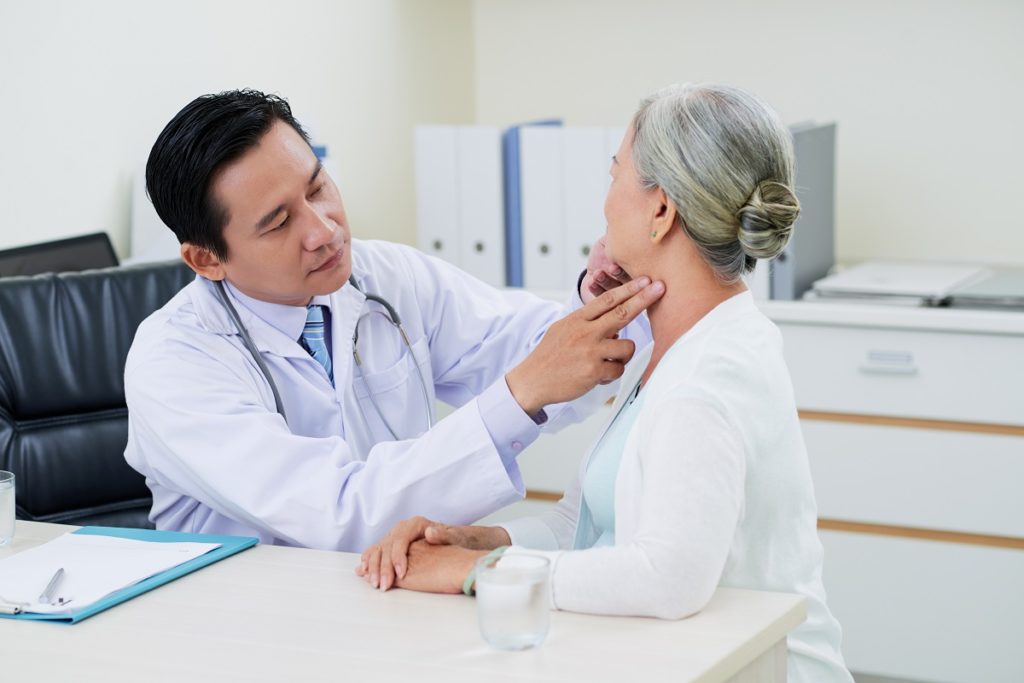
The clinical history and physical examination play an important role in the diagnosis of hypothyroidism. However, further laboratory testing and imaging are necessary to confirm the diagnosis. An endocrinologist often requests thyroid function tests to detect hormone deficiencies. Low thyroid hormone levels of free T3 and T4 as well as elevated TSH denote hypothyroidism. Ultrasound of the neck and thyroid may also be performed to check for possible nodules that may alter normal thyroid functioning.
Hypothyroidism increases the risk of developing several conditions such as obesity, cardiovascular collapse, and osteoporosis. If left untreated, this disease may even cause long-term damage in the different organs of the body. Therefore, it is crucial to visit an endocrinologist who specializes in the early evaluation and treatment of thyroid diseases.