- Acceptance and seeking professional help are crucial first steps towards recovery.
- A robust support system of trusted individuals can greatly aid in managing bulimia nervosa.
- Identifying and understanding triggers, such as emotional, physical, environmental or social, is essential for managing the disorder.
- Mindfulness and self-care practices, including adequate sleep and balanced meals, can promote a healthier relationship with food and the body.
- Committing to a tailored treatment plan guided by healthcare professionals is key for long-term recovery.
Bulimia nervosa is a significant health challenge impacting many lives, with sufferers often feeling trapped in a cycle of bingeing and purging. The journey to recovery is possible, and it starts with understanding the necessary steps to take towards healing and maintaining mental wellness. Below are five practical tips to help you or a loved one navigate bulimia nervosa.
1. Acknowledge and Seek Help
Accepting that you have a problem is the pivotal first step towards recovery. Often, individuals struggling with bulimia nervosa live in denial, which hinders them from seeking the help they need. Acceptance allows you to approach your healing journey with a committed and conscious mindset.
Once you acknowledge the issue, seeking professional help is crucial. Healthcare providers, therapists, or counselors trained in eating disorders can offer invaluable support and resources to set you on a path to recovery.
2. Develop a Support System
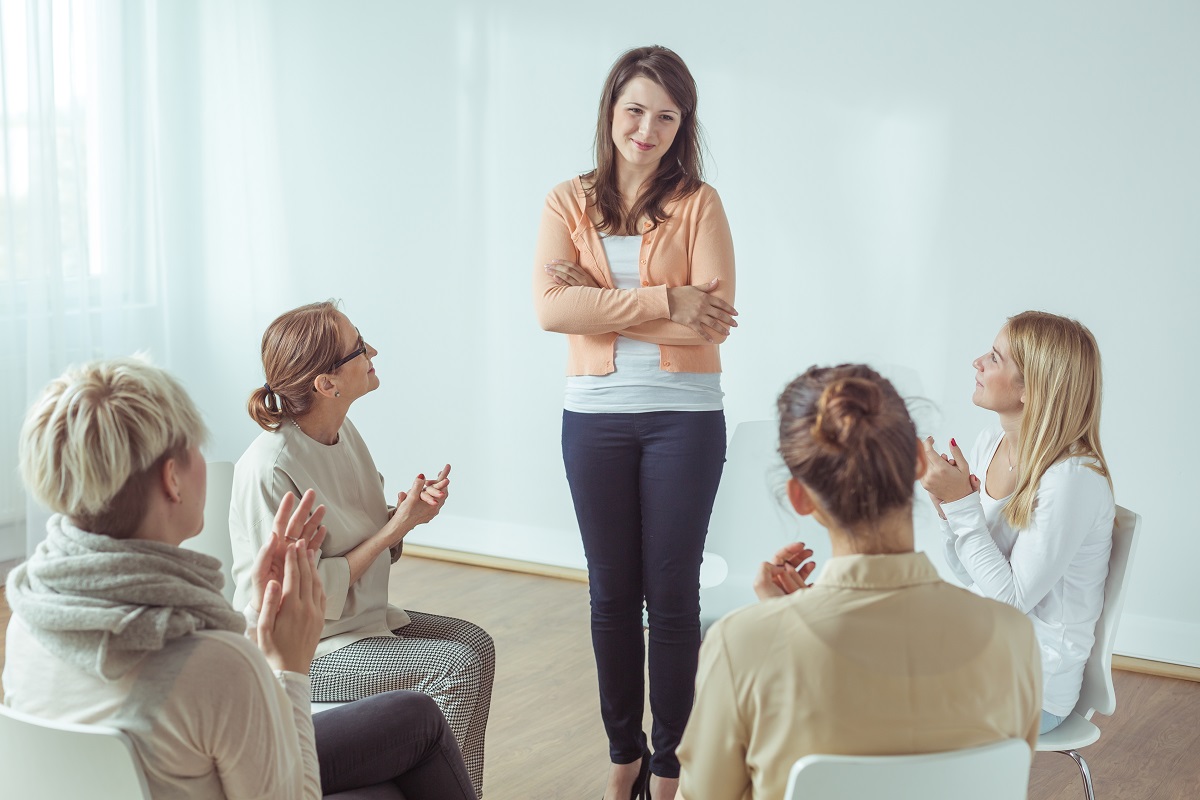

Having a robust support system is vital for anyone battling bulimia nervosa. Engage close family members and friends who are understanding, non-judgmental, and supportive. Sharing your struggles with someone you trust can significantly alleviate the emotional burden of bulimia.
A support system offers encouragement, understanding, and a sense of stability, all of which are crucial during the recovery process. Consider joining support groups where you can connect with others going through similar experiences, fostering a sense of community and shared understanding.
3. Understand Your Triggers
Identifying and understanding your triggers is essential in managing bulimia nervosa. Triggers can be emotional, physical, or environmental, including stress, depression, body dissatisfaction, or even certain social settings. Acknowledging these triggers allows you to develop coping mechanisms that don’t involve turning to food.
With the understanding of triggers, you can actively work on minimizing exposure to these stressors or developing healthier responses, significantly reducing the likelihood of a binge-purge cycle.
Here are some possible triggers for bulimia nervosa in detail:
Emotional Triggers
Emotional triggers can be feelings that arise from personal or interpersonal issues, such as loneliness, depression, stress, or anxiety. These feelings can induce an overwhelming urge to binge, leading to a cycle of compulsive eating and purging. Recognizing these emotional states as potential triggers can help develop coping mechanisms like mindfulness-based exercises or stress management techniques to navigate these emotions healthily.
Physical Triggers
Physical triggers often relate to bodily discomfort or perceived flaws or dissatisfaction with one’s body image. The feeling of fullness, hunger, or body insecurities can trigger a binge-purge episode. Paying attention to your body’s actual needs (like hunger or fatigue) and distinguishing them from bulimia-driven urges can be useful for managing these triggers.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental triggers include situations, places, or even people that contribute to triggering bulimic behavior. This might be a setting where bingeing has occurred in the past, social gatherings around food, or even being around individuals perpetuating harmful body image narratives. Identifying such environmental triggers allows you to prepare for or avoid these situations when possible.
Social Triggers
Social triggers involve dynamics within relationships or societal pressures that can provoke bulimic tendencies. This can stem from toxic relationships, bullying, or societal pressures emphasizing thinness as the standard of beauty. Building resilience towards these social pressures, seeking positive relationships, and fostering a healthier body image can help manage these triggers.
4. Practice Mindfulness and Self-Care
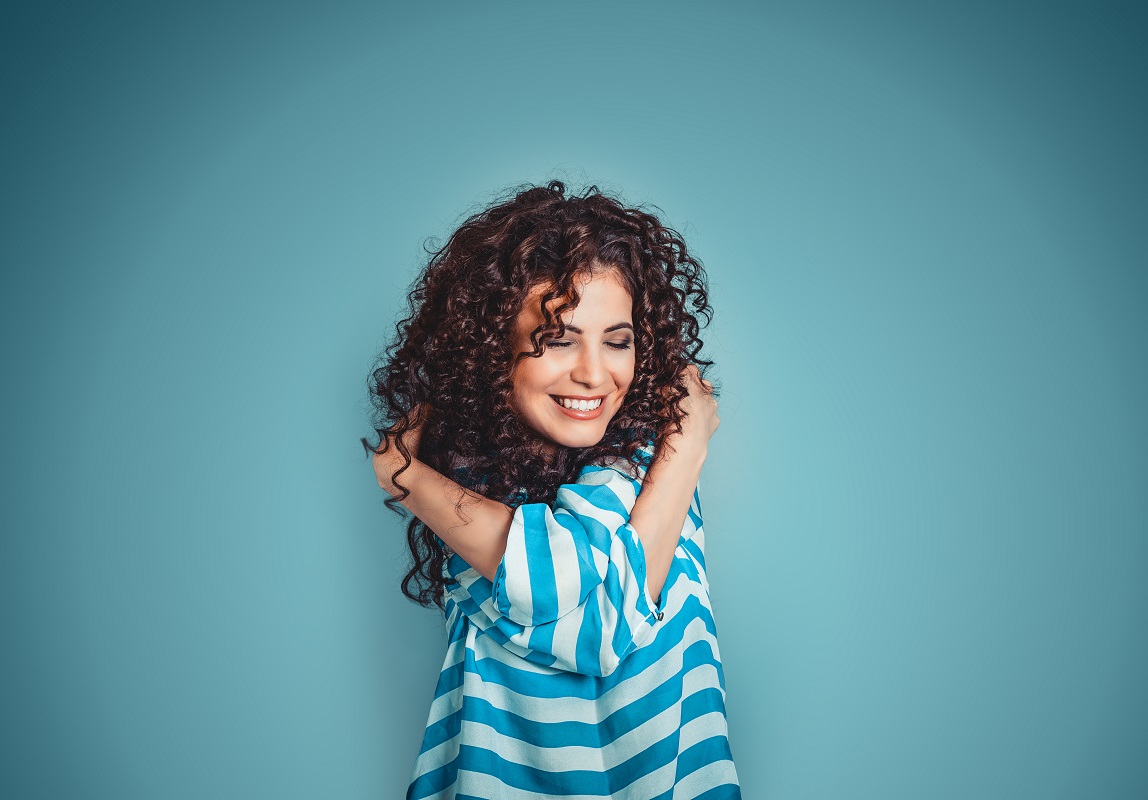

Mindfulness involves staying present and fully engaging in the here and now. This practice can help you develop a healthier relationship with food and your body. Engage in activities that promote relaxation and reduce stress, like yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises.
Prioritize self-care by getting adequate sleep, engaging in enjoyable physical activity, and nourishing your body with balanced meals. Self-care practices foster self-love and respect, which are crucial to recovering from bulimia nervosa.
5. Commit to a Treatment Plan
Following a professionally-guided treatment plan for bulimia nervosa is paramount for recovery. Your healthcare provider will develop a plan tailored to your needs, often incorporating therapy, medication, and nutritional counseling. Committing to this plan requires discipline, persistence, and a willingness to reclaim your health and happiness.
A treatment plan for bulimia nervosa is not a one-size-fits-all; it is often adjusted over time to align with your evolving needs and progress. Regularly communicating with your healthcare provider ensures you receive the right support at every stage of your recovery.
To Wrap It Up
Recovery from bulimia nervosa is undoubtedly challenging but attainable with the right mindset, support system, and professional guidance. Acknowledge your struggles, seek help, understand your triggers, practice mindfulness, and commit to a treatment plan to navigate you through recovery. Each step you take towards healing is a victory, and with time and effort, a healthy and fulfilling life is within reach.