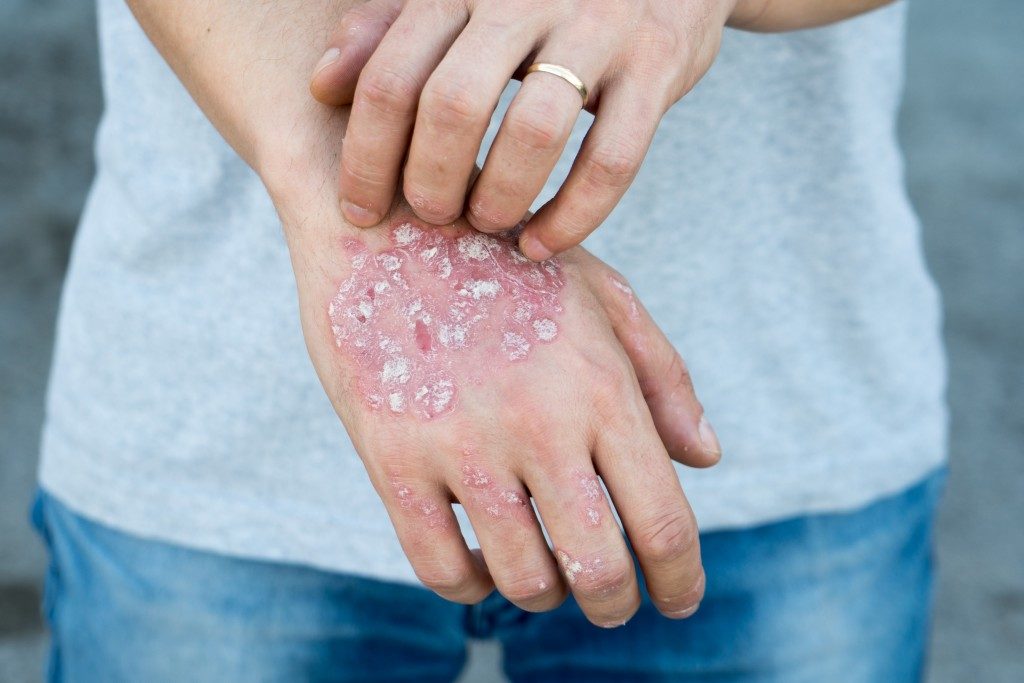
Autoimmune disorder or disease is an umbrella term used for describing hundreds of diseases; most notably type 1 diabetes, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, in which the immune system of body attacks its own tissues and cells. Plenty of studies have shown that certain genetic factors combined with environmental factors are to blame for most autoimmune diseases, notes a prominent autoimmune disease treatment expert in Logan. However, researchers are still trying to figure out other factors that might contribute to the risk of developing autoimmune diseases.
Who’s at Risk for Developing Autoimmune Diseases?
These factors can increase your risk of developing an autoimmune disease:
- Being young or middle-aged. Majority of autoimmune diseases impact younger individuals and middle-aged individuals. Do note though that some diseases, specifically rheumatoid arthritis, are much more common in aging individuals.
- Being female. Unfortunately, studies have shown that females are more predisposed to autoimmune diseases than males. While the reason isn’t exactly clear, studies suggest that it might be due to the hormonal makeup and enhanced immune systems of females.
- A history of autoimmune disease in the family. Having a family member who has an autoimmune disease will increase your risk of developing the same disease or one that’s similar or closely related to the disease.
- Being of Latino, African American, and American Indian descent also increase your chances of developing an autoimmune disease.
- Being exposed to certain environmental agents. According to a study published in the Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, there’s evidence to support that being exposed to specific environmental agents might increase your chances of developing autoimmune diseases. For instance, research has shown that exposure to mercury, silver, or gold, and certain drugs such as hydrolyzine and procainamide might be associated with an increased risk of developing autoimmune diseases.
- Past infections. Lots of evidences support the finding that some individuals who’ve been previously infected with certain viral and bacterial infections might have an increased risk of developing certain autoimmune diseases.
Is it Possible to Reduce The Risk of Developing an Autoimmune Disease?
Because the causes of various autoimmune diseases have yet to be identified and due to risk factors that cannot be controlled, it’s hard to determine whether or not it’s possible to reduce your chances of developing an autoimmune disease. But as researches learn more and more about the association between previous viral and bacterial infections and its part in the development of certain autoimmune diseases, you can try to lower your risk by reducing your risk of getting infected with viral and bacterial infections. For starters, ensure that you wash your hands properly by vigorously rubbing them together with warm water and soap for 15 seconds. You also need to steer clear of sick people who can infect you and ensure that your vaccinations are up-to-date.
In the event that you are worried that you might be highly susceptible to developing autoimmune diseases because one or more of the risk factors mentioned above apply to you, consult your doctor. Your doctor will perform certain tests to try to figure out if you do have an autoimmune disease.