Insurance is required in most countries to start a large-scale business. In most cases, companies add more to their insurance coverage than what’s needed as they understand the importance of being protected against losses. A few of these required and additional insurance products include:
Insurance is required in most countries to start a large-scale business. In most cases, companies add more to their insurance coverage than what’s needed as they understand the importance of being protected against losses. A few of these required and additional insurance products include:
Gap Insurance
Part of your company’s growth is reliant on the health of your employees. Health insurance is mandatory for most companies. Some offer high deductible health plans, while other companies provide medical gap insurance to regular workers of their company.
Gap insurance, or insurance on insurance, cover medical costs before a deductible level could be reached. Coinsurance expenses, copayments, deductibles, living expenses during a hospital stay or recovery, and prescription drugs are covered by various gap insurance structures. Medical gap insurance is also cheaper than a health savings account.
Fire Insurance
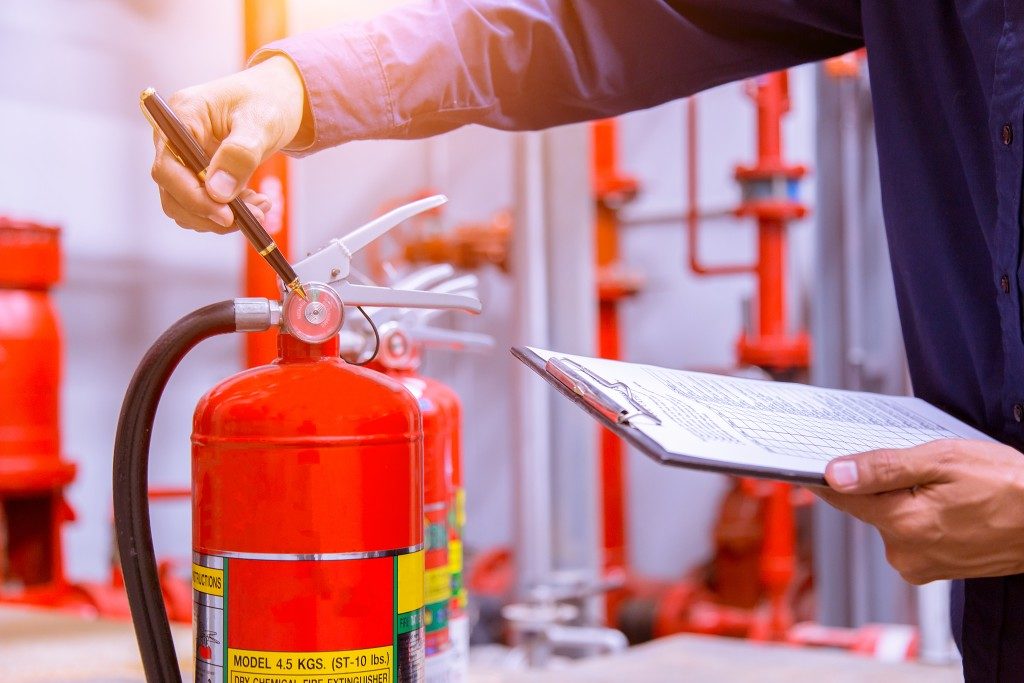 One of the first types of insurance that business owners take, fire insurance protects buildings and any fixtures within—except for cash and jewelry—from any loss or damage from fire. Fire insurance can be extended to protect properties from fire resulting from earthquakes, typhoon or flood, vehicle impact or falling aircraft, explosions, smoke damage, and malicious strikes by workers.
One of the first types of insurance that business owners take, fire insurance protects buildings and any fixtures within—except for cash and jewelry—from any loss or damage from fire. Fire insurance can be extended to protect properties from fire resulting from earthquakes, typhoon or flood, vehicle impact or falling aircraft, explosions, smoke damage, and malicious strikes by workers.
In the U.S. alone, fire insurance helped cover for approximately $10.7 billion of damages caused by fires. Business owners who wish to avoid being part of those expenses and want to avoid being hit by penalties due to underinsurance should insure their property completely.
Business Owner’s Policy (BOP)
Often advertised to small-business owners first, BOPs are good policies to take, especially if companies are low-risk and qualify for other criteria. The small business insurance package offers a couple of products for a discounted rate. BOPs package together general liability and commercial property insurance, putting small business owners in a great advantage in terms of cost.
The insurance bundle is most beneficial for clients whose service may accidentally damage a client’s property, cause a fire at their place of business, or injure a worker or client. Accidents incurred by clients at the business owner’s property will also be paid for. Moreover, severe weather events, theft, and vandalism are also accounted for in this bundle.
Property Insurance
Warehouses, rented offices, and other structures are typically protected by this type of insurance. Property protection or liability coverage can include flood and earthquake insurance, as well as homeowners and renters insurance. Weather-related incidents such as hail, fire, wind, lightning, and man-made incidents like vandalism and theft are also covered.
Extreme circumstances such as terrorist attacks are not covered. Damage borne from neglect, such as mold, leaking groundwater, and sewer backups is not covered either. Damage from earthquakes and tsunamis are also not covered by property insurance.
Business owners may opt for three types of property insurance: actual cash value, extended replacement costs, and replacement costs. Depreciation is deducted from the replacement cost in actual cash value coverage. Replacement cost values are paid back under replacement cost coverage.
When shopping for new insurance, business owners must research what their company or employees need. Owners must know how to balance cost effectiveness with coverage and if their employees want to co-pay to get to a higher tier of insurance. Risk pooling, the basis of insurance, is crucial to cut down out of pocket expenses and protect the assets of a business owner.